Introducing the Charge Recursive Neural Network (QRNN)
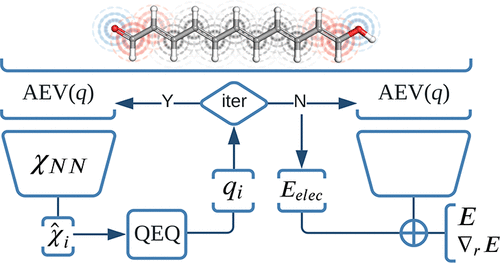
In recent years, a new class of methods called neural network potentials (NNPs) has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional force-fields. NNPs are trained on a dataset of reference calculations to learn the relationship between the atomic structure and the energy of a molecule. Once trained, NNPs can be used to simulate molecules much more efficiently than traditional methods.
One of the challenges with NNPs is that they can be difficult to transfer to new types of molecules. We have developed a new NNP architecture called QRNN, which predicts atomic charges and uses these charges as descriptors in an energy model. We have shown that QRNN can accurately predict the conformational energies of ionic and zwitterionic druglike molecules with chemical accuracy.
We believe that transferable NNPs have the potential to revolutionize drug discovery by making it possible to simulate large-scale ensembles of molecules at an unprecedented level of accuracy. This could lead to the discovery of new drugs more quickly and efficiently.
Check out the full work here