QRNN for Liquid Electrolyte Simulation
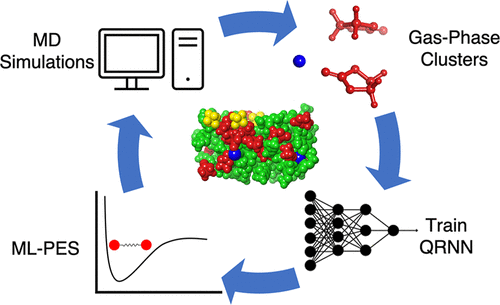
Li-ion batteries are the workhorses of the modern world, powering everything from smartphones to electric cars. One of the key challenges to improving Li-ion batteries is developing better liquid electrolytes, which are the solutions that ions flow through inside the battery.
To improve liquid electrolytes, we need to be able to accurately calculate their properties, such as viscosity and ionic diffusivity. However, traditional atomistic calculations are very computationally expensive and don’t have the accuracy required to make experimental decisions.
We have trained a machine learning-based force field on a dataset of non-periodic DFT calculations. This allowed us to use a very accurate theory (ωB97X-D3BJ/def2-TZVPD) to train our model, which would be prohibitively expensive for generating large datasets with periodic DFT.
We have tested our force field on seven common carbonates and LiPF6, and it was able to accurately predict the properties of these materials. We are hopeful that we can apply this kind of force field to a wide range of liquid electrolyte systems in the future.
Check out the full work here